Finding the Right Balance: Is It Good to Use Retinol Every Day?
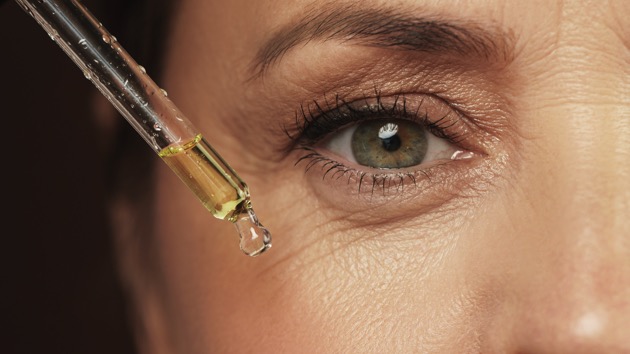
Recognized as a cornerstone in skincare, retinol offers a multitude of advantages. Its capabilities include stimulating skin cell production, clearing pores, exfoliating, and promoting collagen production to combat the development of fine lines and wrinkles. Additionally, many retinoids can help fight acne. But here’s the question many retinol users ask: is it good to use retinol every day?
This versatility positions it as a remarkable multitasker. Accessible in strengths ranging from prescription to over-the-counter, and in formats such as serums and moisturizers, retinol’s popularity raises the question of whether there can be an excess of this beneficial ingredient.
To explore this, we seek insights from dermatologists, estheticians, and holistic skincare experts, delving into the world of retinol.
Understanding Retinol
Retinol, derived from vitamin A, plays a crucial role in regulating skin cell turnover and enhancing collagen production. Its effectiveness extends to improving skin tone, reducing discoloration, and addressing fine lines and wrinkles.
Not all Retinols Are Created Equal
While synthetic, prescription-based retinol may be preferred for its strength and rapid results, plant-based alternatives often appeal to those seeking a less aggressive and healthier long-term alternative. The choice between the two hinges on individual preferences and skin sensitivity.
For those with sensitive skin and those who want to avoid skin irritation from a prescribed retinol, Plant Mother’s organic Retinol serum is a perfect solution. It is packed with plant-based vitamins, carotenoids, and antioxidants to feed your skin and stimulate collagen production.
Additionally, if you have mature skin, it typically tends to be on a dryer side and needs more nutrition than a young skin. Therefore, a healthier and less drying plant-based retinol is better for these types of skins too.
For Anna De La Cruz, a master esthetician, the fact that plant-based retinol addresses so many of the same skin concerns as prescription retinol—without the potential side effects—gives it a leg-up as a treatment for most types of skins. “Usually sensitive skin and eczema-prone skin cannot tolerate retinol,” she says. “As skin ages, it tends to become dryer and more sensitive, making bakuchiol a fantastic alternative, especially for mature skin.”
check out Best sellers:
Is it good to use retinol every day?
While nightly use of retinol is usually the norm, a cautious initiation is recommended with synthetic prescription-based retinoids. It’s good to start with a few applications per week. This allows you to assess your skin’s tolerance.
On the other hand, plant-based and bakuchiol alternatives can be used nightly and don’t require gradual initiation or increase of dosage over time.
Choosing the Right Amount and Type
The ideal type and amount of retinol depends on individual skins and concerns. It is a good idea to apply a pea-sized amount of retinol. This is generally considered sufficient for most individuals. If it’s a serum, a few drops nightly are usually enough. Less is more with retinols. Patience is key, as tolerance builds over time, minimizing the risk of inflammation and irritation. And remember, each skin is different, so make sure you “listen” to your skin.
Potential Side Effects
According to a NYC based board-certified dermatologist Doris Day, “when using a Vitamin A product, it can be difficult to dose correctly without the dreaded side effects, which include skin sensitivity, redness, irritation and even a flare-up of breakouts as the skin adjusts to the ingredient.”
The duration of these symptoms typically lasts a couple of weeks to a month, but sometimes the symptoms stay in a gentler form (redness and dryness). As mentioned above, non-synthetic retinols, such as a completely plant-based Retinol serum, are perfect for those who don’t want or can’t deal with harsh side-effects of prescription-based and synthetic retinols.
Possible Issues and Remedies
Excessive use of harsh retinol may lead to skin purging or retinol burn, characterized by irritant contact dermatitis. In such cases, discontinuing retinol use allows the skin barrier to recover. You should switch to a plant-based retinol after your skin is healed.
Additionally, you should practice gentle skincare, including mild cleansers and hydrating ingredients. This helps in the recovery process. An ideal skin care routine would be to apply a nourishing plant-based Vitamin C serum daily and use a plant-based Retinol at night.
In conclusion, retinol, an essential anti-aging ingredient, yields long-term benefits by enhancing cell turnover and stimulating collagen production. Make sure you choose the right retinol for your skin type. This will help you avoid unnecessary skin irritation and dryness.
You should always apply small amounts of retinol because it is a powerful ingredient. Adhering to a consistent skincare routine, incorporating sunscreen, and being mindful of potential irritation are crucial aspects of using retinol effectively.
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
This content is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to provide medical advice or to take the place of such advice or treatment from a personal physician. All readers of this content are advised to consult their doctors or qualified health professionals regarding specific health questions. The publisher of this content does not take responsibility for possible health consequences of any person or persons reading or following the information in this educational content. All viewers of this content, especially those taking prescription or over-the-counter medications, should consult their physicians before beginning any nutrition, supplement, skincare product, or lifestyle program.



